
Understanding Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction
Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction (TMJ) involves issues with the jaw joint and muscles controlling jaw movement. It can arise from various factors including jaw injury, arthritis, or excessive jaw clenching. TMJ often leads to discomfort or pain in the jaw joint and surrounding tissues.
The condition may also be influenced by genetics, hormonal changes, or poor posture. Stress and certain habits like teeth grinding can exacerbate the issue. It can affect eating, speaking, and other jaw movements, impacting daily life. Management often involves a multidisciplinary approach to address the complex nature of the disorder.
Early diagnosis is crucial as TMJ can result in chronic pain and limited jaw functionality if untreated. Symptoms vary widely, ranging from mild discomfort to severe pain. Properly addressing TMJ requires a comprehensive approach, considering both physical and sometimes psychological factors contributing to the dysfunction.
Book ConsultationSymptoms of Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction
The symptoms of Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction (TMJ) are diverse, affecting the jaw and areas around it. This condition can lead to significant discomfort during daily routines like talking and eating. Symptoms often manifest gradually, becoming more noticeable over time. Individuals may experience discomfort while chewing or a limited range of jaw motion, impacting daily activities.

Jaw Pain
Persistent pain in the jaw area that might intensify during jaw movements.

Clicking Sounds
Audible clicking or popping noises when opening or closing the mouth, often painless.

Lockjaw
The jaw may lock or get stuck while opening or closing, causing discomfort.
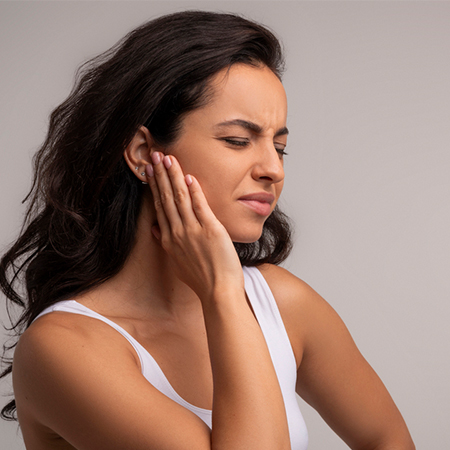

Ear Pain
Pain can radiate to the ears, often mistaken for an ear infection.
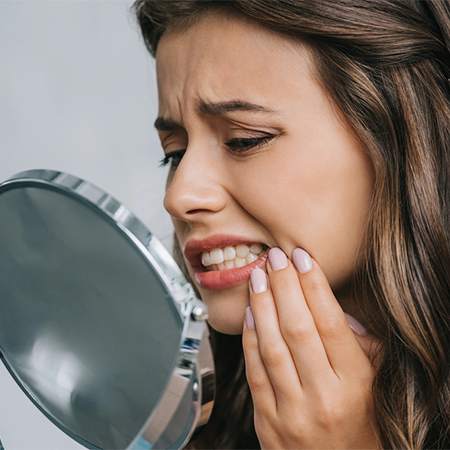

Difficulty Chewing
There may be pain or discomfort while chewing, affecting how one eats.
Treatment Options for Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction
Treatment for Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction (TMJ) aims to relieve pain and restore normal jaw function. Options range from self-care practices to medical interventions depending on the severity of the symptoms. Addressing TMJ effectively often requires a combination of therapies to reduce stress on the jaw and alleviate symptoms.
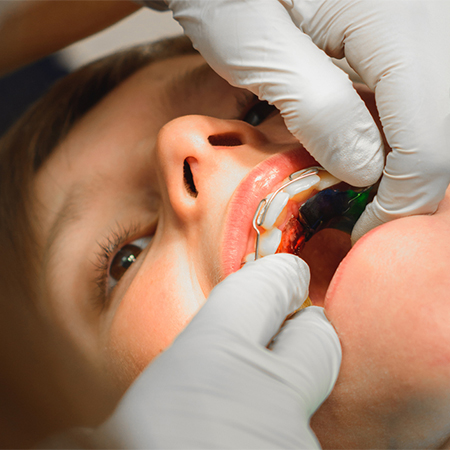
Oral Appliances
Dentists may prescribe mouthguards or splints that help align the jaw and prevent teeth grinding, which can exacerbate TMJ symptoms. These devices are worn mostly at night and can significantly reduce strain on the jaw muscles and joints. Consistent use can lead to long-term improvements in jaw alignment and pain relief.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy includes exercises to strengthen jaw muscles, improve mobility, and teach relaxation techniques. Therapists might also use ultrasound therapy or moist heat to reduce pain and stiffness in the jaw area. Regular sessions help patients manage symptoms effectively and prevent further complications.